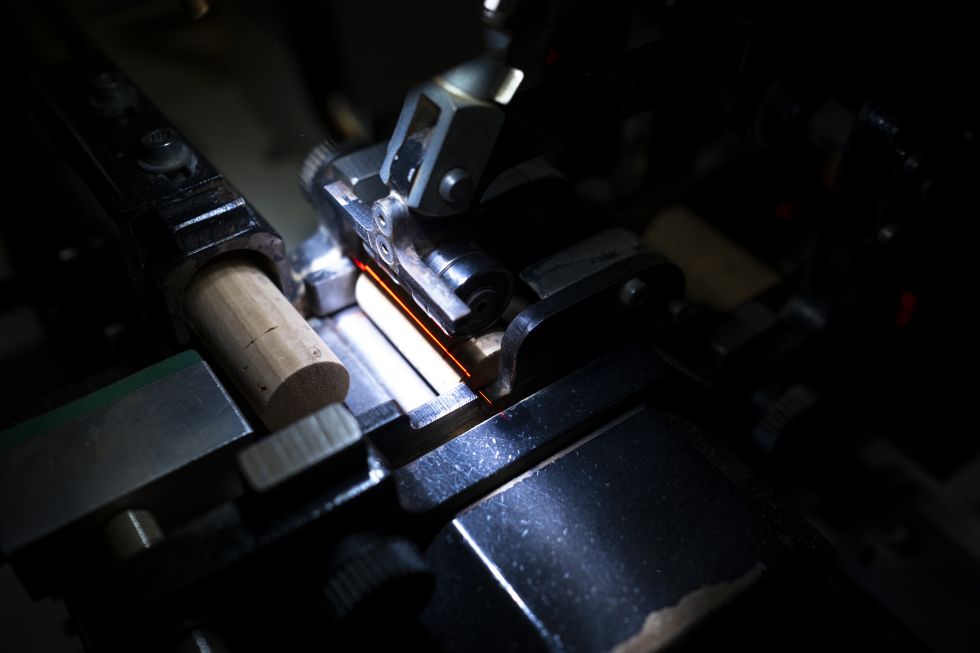
The production of natural cork stoppers goes through several stages. The most important of these are drilling - when the strip of cork is perforated to create a one-piece cork stopper - and selection - the meticulous sorting of cork stoppers into different classes.

Drilling
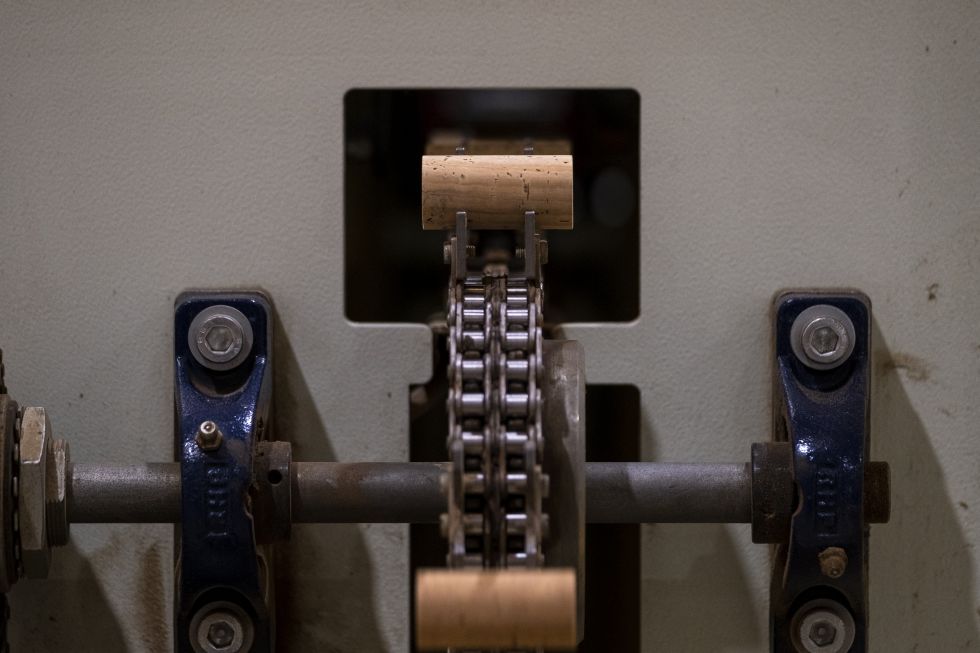
Drilling is the manual, semi-automatic or automatic process of perforating cork strips with a drill. This produces a cylindrical cork stopper that complies with the desired dimensional limits. All the waste from the drilling stage is used to make cork granules. The cork that doesn't lead directly to the natural cork stopper, the top of the range of stoppers, will be used for granulating and making technical stoppers or to manufacture agglomerated cork products that are used in insulation or as a construction, decoration and design material.
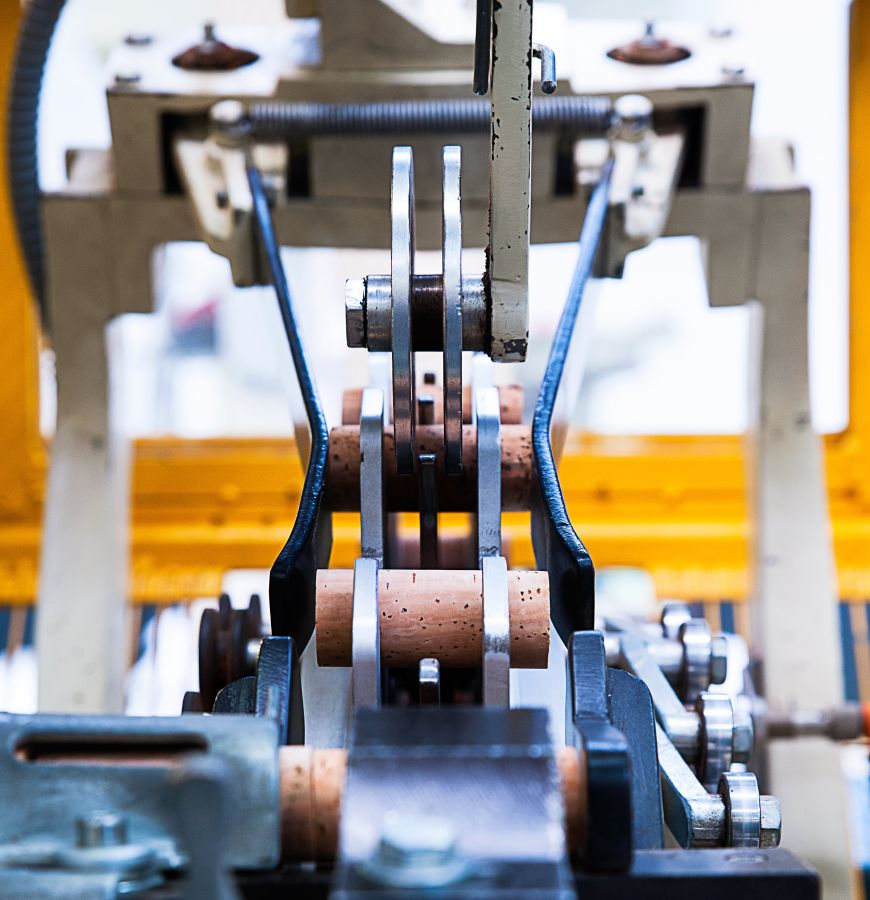
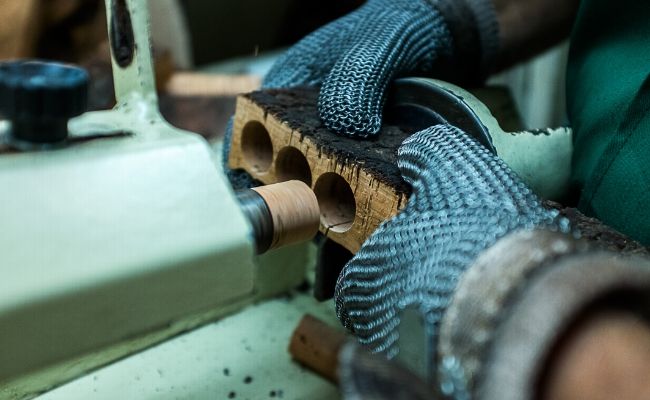
Rectification
After drilling, the process of rectification is used to obtain the final dimensions previously specified and to smooth the surface of the cork stopper

Selection
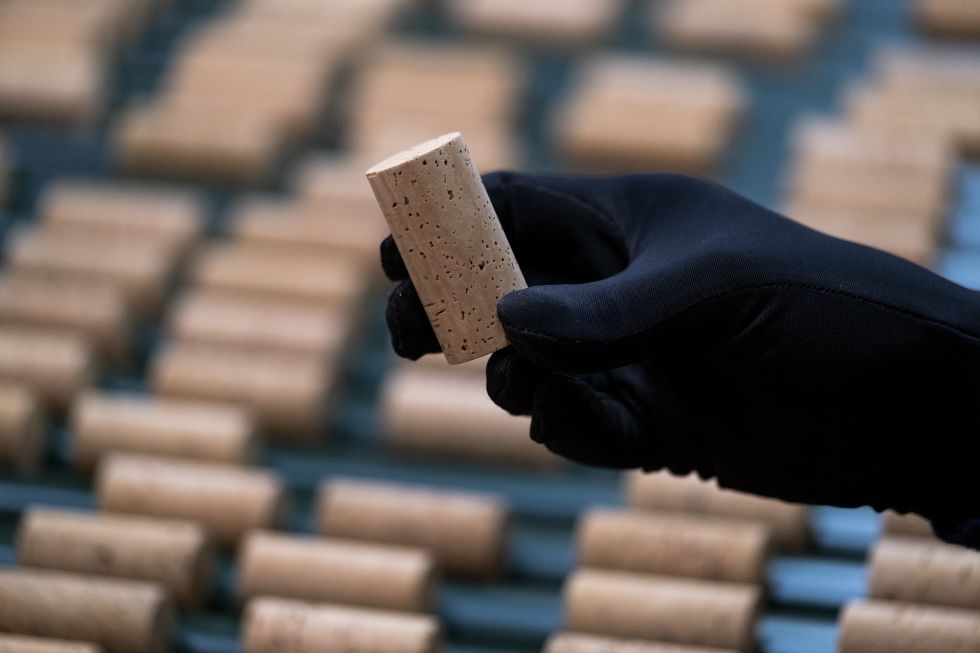
Commonly known as sorting, this is the operation designed to separate the finished stoppers into different classes, with each class being determined by automatic control of the surface of the stoppers. In some cases, sorting is done visually and manually, using the skill of the human eye. During this phase, in addition to defining the qualities, corks with defects are also eliminated.
Washing
After rectification, the corks are washed using hydrogen peroxide or paracetic acid. This bath is used to clean and disinfect the stoppers, but other methods such as microwaves or ozone can also be used.
After washing/ disinfection, the moisture content is stabilized, thus optimizing the performance of the stopper as a seal and reducing microbiological contamination.
After washing/ disinfection, the moisture content is stabilized, thus optimizing the performance of the stopper as a seal and reducing microbiological contamination.
Colmating
Occasionally, stoppers can be colmated, giving origin to colmated cork stoppers. Colmating consists in filling the pores on the surface of the cork stoppers (lenticels) with a mixture of cork powder resulting from the rectification or grinding of natural cork stoppers. A natural resin-based glue and a water-based glue are used to fix the powder in the pores (lenticels). Colmating improves the visual appearance of the cork stopper and its performance.

Branding
This operation is carried out according to the client's instructions for the type of branding to be applied. Printing methods include ink printing (food-grade), flame or laser marking.
After being branded, the surface of the stopper is treated with paraffin or silicone to make it easier to insert into the bottle and for the end consumer to remove it.
After being branded, the surface of the stopper is treated with paraffin or silicone to make it easier to insert into the bottle and for the end consumer to remove it.
Packaging and Transportation
When production is complete, the stoppers are packed in plastic bags filled with SO2 (sulphur dioxide), a gas that inhibits microbiological growth. Only then will they be transported to the wine or spirits bottler. Other forms of packaging are being implemented to optimize transportation, however, this remains the most common.